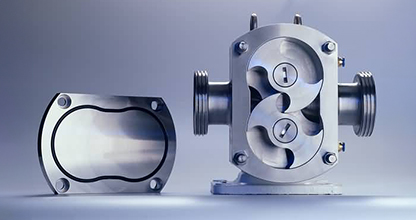
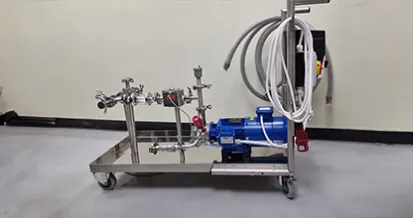
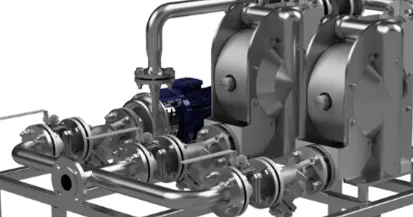
Tapflo has a large range of Centrifugal Pump available to our customers including our CT range of Centrifugal Pumps. The CT Range features the CTH and CTI Pumps. The CTH range is Tapflo’s Hygienic Centrifugal Pump and the CTI range is the Industrial Centrifugal Pump range.
Installation Example
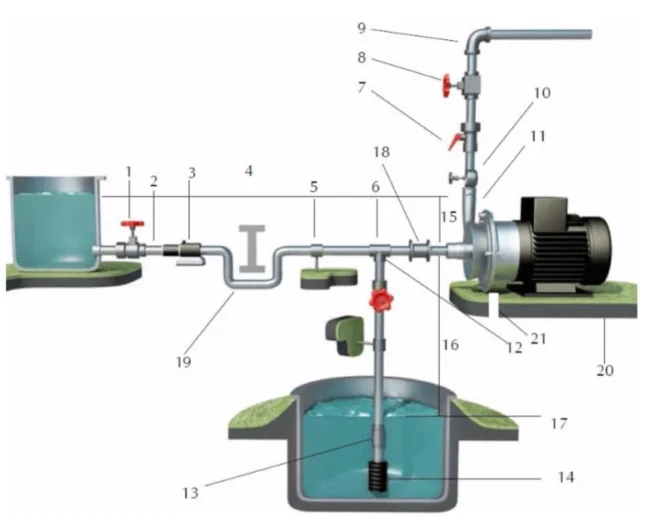
| Number | Permissible | Detail |
| 1 | YES | Gate Valve – may also be fitted closer to the pump in case of long pipework |
| 2 | N/A | With a positive suction head tilt the pipework towards the direction of the pump inlet |
| 3 | YES | In-Line Strainer – required if there are particles present, larger than 6mm |
| 4 | NO | Air Pockets – the circuit needs to be as short and as straight as possible |
| 5 | YES | Pipe connectors |
| 6 | N/A | Suction line needs to be as short and direct as possible, ideally the same size as the pump inlet or 1 size larger. |
| 7 | YES | Attachment for Pressure Gauge or Pressure Relief Valve. It is best practice to install a Pressure Gauge on the discharge of the pump to evaluate where it is working on its curve. A Pressure Relief Valve is required when there is a possibility for “Dead Head” operation or when using a nozzle for example. |
| 8 | YES | Gate Valve – useful for regulating the performance of the pump |
| 9 | Bends in the pipework need to be ideally placed after any valves and instrumentation and ideally placed five times the ø of the pipework away. I.e. if the pipework is 25mm then any bends would ideally need to be placed 125mm away from the pump and any valves or instrumentation. | |
| 10 | YES | Attachment for Pressure Gauge or Pressure Relief Valve. It is best practice to install a Pressure Gauge on the discharge of the pump to evaluate where it is working on its curve. A Pressure Relief Valve is required when there is a possibility for “Dead Head” operating or when using a nozzle for example. |
| 11 | NO | Elbow Joints & other bends on the pump suction or discharge ports |
| 12 | N/A | When operating the pump in a suction lift application, ensure that the suction pipework is as short as possible and contains as few bends as possible. Also ensure that a Non-return or Check Valve is installed at the pump inlet or at the bottom of the suction pipe. |
| 13 | YES | Check Valve/Non-return Valve – essential when operating a suction lift application |
| 14 | YES | Suction Strainer – essential when there is a the potential for solids in suspension larger than the capability of the pump. |
| 15 | N/A | |
| 16 | N/A | Suction Head – the distance between the pump inlet and the surface of the fluid. This needs to be no more than the capability of the pump in question. |
| 17 | N/A | Immersion depth – the distance between the surface of the fluid and the bottom of the suction pipe. |
| 18 | YES | Expansion joint – indispensable with long pipework and/or hot liquids. Anti-Vibration Facility – considered best practice when using the pump on a fixed & rigid pipework. |
| 19 | YES | Overcome obstacles on both the suction and discharge by lowering the pipework where possible. Essential on the suction side, ideal on the discharge side. This reduces the work the pump has to overcome as well as eliminating the possibility of air pockets. |
| 20 | N/A | Fix the pump into the installation by the fixing holes provided, the supports and/or base must be level |
| 21 | YES | Drainage channel – it is best practice to allow for a drainage channel around the base of the pump to allow for easy drainage of the pump without contaminating the installation. Pumps can be supplied with drainage valves/ports and/or drainage facilities on their base frames or trolleys. |