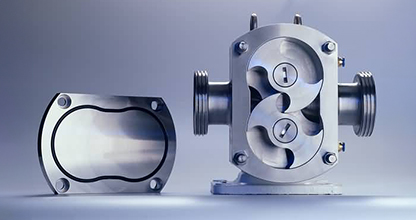
Magnetic Drive Pumps use magnetic coupling to transfer power from the motor to the impeller, eliminating the need for a mechanical seal, thereby preventing leaks and ensuring a hermetically sealed and safe fluid transfer in various applications. This versatility and safety make Magnetic Drive Pumps integral in industries such as Chemical, Surface Treatment, Mechanical, Paint and Wastewater.
In this blog, we’ll share important insights into Magnetic Drive Pumps and their significance in various industries. We’ll look at their versatility, unique features and advantages, with the aim of providing you with a better understanding of their role and areas they excel in.
What is a Magnetic Drive Pump?
Magnetic Drive Pumps, also known as Magnetically Driven or Mag Drive Pumps, employ a magnetic coupling system. This system consists of two essential magnets; one located externally, known as the drive magnet, and the other positioned internally. Together, these magnets play a crucial role in the operation of Magnetic Drive Pumps.
The operational principle of Magnetic Drive Pumps is relatively simple but highly effective. Instead of the traditional pump design with a shaft penetrating the outer casing, Mag Drive Pumps adopt a hermetically sealed chamber and sealless construction. This design ensures an airtight, leak-free environment within the pump, preventing the escape of fluids or vapours into the surrounding area.
In industries dealing with aggressive and corrosive fluids, such as the Chemical industry, the hermetic sealing of Magnetic Drive Pumps is of utmost significance. Their robust construction makes them ideal for applications where fluid containment is critical. This feature is especially valuable for companies handling expensive or hazardous chemicals, where any leak could result in safety hazards and substantial financial losses.
How do Magnetic Drive Pumps Work?
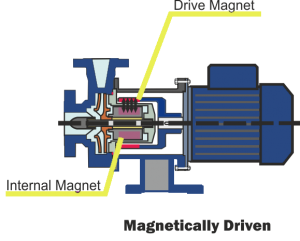
Magnetic Drive Pumps use two magnets to move liquids without physical contact between the motor and impeller. The external magnet, connected to the motor shaft, is attracted to an internal magnet enclosed within the pump. When the motor shaft rotates, the magnets’ opposing polarities cause the internal magnet to spin. This motion is transferred to the impeller, which propels the liquid.
The hermetic, sealless design ensures safe and efficient fluid transfer without leaks or physical connections. Magnetic Drive Pumps are favoured for their precision, reliability and safety in fluid handling.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Magnetic Drive Pumps
Advantages of Mag Drive Pumps:
- Magnetic Drive Pumps are essentially leak-proof. They eliminate the risk of hazardous chemical spills and prevent expensive product wastage when operated properly
- These pumps are known for their simple design which offer reliability and minimal maintenance requirements, which in turn reduces downtime and operating costs
- Magnetic coupling eliminates the need for complex motor and pump alignment procedures, saving time during installation and maintenance procedures
- Magnetic Drive Pumps are designed to meet strict environmental and safety standards, making them suitable for applications that require adherence to regulations
- With fewer working parts, Magnetic Drive Pumps typically have longer working life spans. Additionally, their simplicity makes them easier to disassemble and maintain, further extending their life cycle
At Tapflo UK, we offer a wide range of Magnetic Drive Pumps sourced from reputable manufacturers like Gemme Cotti and Yildiz Pompa, ensuring that our customers have access to top-quality fluid handling solutions.
Disadvantages of Magnetic Drive Pumps:
- Magnetic Drive Pumps are best suited for handling clean fluids. They aren’t recommended for applications involving fluids with significant solids content, as this can lead to wear and reduced efficiency
- When compared to standard Centrifugal Pumps, Magnetic Drive Pumps commonly consume more power. This is a consideration for energy efficiency and operating costs, especially in high-flow or high-pressure applications
- It’s important that you carefully assess your specific fluid-handling needs and the nature of the liquids you will be handling to determine whether the advantages of Magnetic Drive Pumps outweigh any potential disadvantages.
Applications of Magnetic Drive Pumps
Our range of Mag Drive Pumps can be used in almost any industry, including both Sanitary and Industrial applications. Take a look to see just how versatile these pumps can be:
- Chemicals
- Surface Conditioning
- Food and Beverage
- Photo Processing
- Mechanical
- Water Treatment
- Hazardous and Corrosive Liquids
- Cryogenics
- Tank Cleaning
- Tank-to-Tank Transfer
- Dispensing
- Pressure Boosting
- Loading and Offloading
- Metering
- Batching
The versatility and reliability of Magnetic Drive Pumps make them valuable assets in a wide range of industries and applications, providing efficient and safe fluid handling solutions.
Key Features to Consider when Selecting a Magnetic Drive Pump
Here’s a list of important features and considerations when selecting a Magnetic Drive Pump:
- Ensure that the materials used in the pump construction are compatible with the fluids you will be handling. This is critical to prevent corrosion or chemical reactions
- Determine the required flow rate (capacity) and the maximum operating pressure of the pump to meet your process needs
- Consider the temperature range of both the fluid being pumped and the ambient operating environment. Ensure the pump can handle the required temperature conditions
- Check if the pump is resistant to the corrosive or aggressive nature of the fluids it will handle
- Verify that the pump has a sealless design to eliminate the risk of leakage associated with conventional pumps
- Ensure the pump offers a hermetically sealed chamber to prevent any fluid leakage or vapour escape
- Consider the energy efficiency of the pump to minimise operational costs over time
- Some applications may require the pump to be self-priming, meaning it can start pumping without external priming assistance
- Verify that the pump’s NPSHr is within the available NPSHa in your system to prevent cavitation
- Assess how easy it is to access and maintain the pump as pumps with fewer complex parts and easy disassembly requirements are easier to maintain
- Consider the noise level produced by the pump, especially if it will be operating in a quiet environment or near workers
- Ensure that the pump can be easily mounted and installed in your system, taking into account space constraints and alignment requirements
- Check for safety features like overheat protection, thermal shutdown and pressure relief valves to safeguard the pump
- Ensure that the pump meets industry standards and regulatory requirements for your specific application
- Consider the initial cost of the pump and evaluate it in conjunction with expected maintenance costs and energy consumption over the pump’s lifespan
- Determine if the manufacturer offers customisation options to tailor the pump to your specific needs
By carefully assessing these key features and factors, you can make an informed decision when selecting a Magnetic Drive Pump that best suits your application requirements and ensures efficient and reliable fluid handling.
Maintenance & Care Tips
Maintaining and caring for Magnetic Drive Pumps is crucial to ensuring their long-term reliability and to prevent unexpected downtime or failures. Here are some maintenance tips and the importance of routine inspections and preventative maintenance:
- Conduct routine visual inspections of the pump and its components to check for any signs of wear, damage or leaks, specifically looking for corrosion, cracks or unusual vibrations
- Regularly inspect and tighten bolts, nuts and fasteners to ensure they are secure as loose fasteners could lead to misalignment and potential issues
- Examine the integrity of seals and gaskets regularly. Replace any damaged or deteriorated seals to maintain the pump’s hermetic seal and prevent leaks
- If your pump uses bearings, ensure they are properly lubricated according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Over or under-lubrication can lead to premature bearing failure
- Keep an eye on the operating temperature of the pump. Abnormally high temperatures could indicate issues with the motor or pump and should be investigated quickly
- Check the condition of the magnetic coupling components. Any damage or deterioration should be addressed promptly to maintain the pump’s efficiency
- Regularly inspect the motor for signs of overheating, unusual noise or vibration and address any motor-related issues to prevent motor failure
- Ensure that the pump’s inlet is not clogged with debris or sediment as this can reduce pump efficiency and increase the risk of cavitation
- Adhere to the manufacturer’s maintenance recommendations and guidelines provided in the pump’s manual
The Importance of Routine Inspections and Preventative Maintenance:
- Routine inspections and preventative maintenance help identify potential issues before they lead to pump failure. Addressing problems proactively reduces downtime and production interruptions
- Regular maintenance and care can extend the working life of the Magnetic Drive Pump, saving you the cost of frequent replacements
- Magnetic Drive Pumps are often used to handle hazardous or corrosive fluids. Proper maintenance helps maintain the integrity of the pump’s hermetic seal, preventing leaks that could pose safety risks
- Well-maintained pumps operate more efficiently, reducing energy consumption and operating costs over time
- In some industries, compliance with regulatory standards and safety requirements is mandatory. Routine maintenance helps ensure your pump remains compliant
- Preventative maintenance is generally more cost-effective than emergency repairs or pump replacement. It helps identify and rectify issues while they are still manageable, preventing costly breakdowns
- Knowing that your Magnetic Drive Pump is well-maintained and regularly inspected provides peace of mind, allowing you to focus on your core operations without unexpected pump-related worries
To recap, routine inspections and preventative maintenance are essential practices to keep your Magnetic Drive Pump in optimal condition, reduce downtime, extend its lifespan and ensure the safety and efficiency of your fluid handling processes. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and consult with pump experts if you encounter any issues during inspections or maintenance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Here are some common problems that can be experienced with Magnetic Drive Pumps, along with solutions and troubleshooting tips:
Common Problems:
Cavitation:
Symptoms:
- Cavitation occurs when low pressure at the pump’s inlet causes vapour bubbles to form in the fluid. This can result in noise, vibration and damage to pump components
Solutions and Troubleshooting:
- Check the NPSHa (Net Positive Suction Head Available) to ensure it meets or exceeds the NPSHr (Net Positive Suction Head Required) of the pump
- Increase the size of the inlet pipe or reduce pipe restrictions to improve fluid flow
- Adjust the pump’s operating speed if possible to reduce suction pressure
Overheating:
Symptoms:
- Overheating can lead to pump damage and decreased efficiency. It may be accompanied by abnormal noise or excessive vibration
Solutions and Troubleshooting:
- Ensure the pump is adequately cooled by maintaining proper ventilation and cooling systems
- Check for obstructions in the cooling flow path and clean as necessary
- Verify that the motor is not overloaded; if it is, consider a larger motor or reducing the pump’s workload
Leakage:
Symptoms:
- Any fluid leakage from the pump can indicate a problem with seals, gaskets or the hermetic chamber, which can be dangerous when handling hazardous fluids
Solutions and Troubleshooting:
- Inspect all seals and gaskets for signs of damage or wear and replace them as needed
- Check the integrity of the hermetic chamber, and if it’s compromised, consult a technician to repair or replace the chamber
Vibration and Noise:
Symptoms:
- Excessive vibration and noise can result from misalignment, worn bearings or other mechanical issues
Solutions and Troubleshooting:
- Verify that the pump is properly aligned with the motor and other components
- Inspect and replace worn bearings or other damaged components as necessary
- Ensure that the pump’s foundation is stable and can absorb vibration
Reduced Flow Rate or Pressure:
Symptoms:
- A decrease in flow rate or pressure can indicate a clog, wear or damage within the pump
Solutions and Troubleshooting:
- Check for clogs or obstructions in the inlet or outlet lines and remove them
- Inspect the impeller and other components for wear or damage and replace as needed
- Adjust the speed of the pump if possible to increase flow rate or pressure
Motor Issues:
Symptoms:
- Problems with the motor, such as erratic operation or failure to start, can affect the pump’s performance
Solutions and Troubleshooting:
- Check electrical connections and ensure the motor is receiving the correct voltage
- Inspect the motor for damaged wiring, windings or worn brushes and address any issues found
- If the motor is overheating, consider using a motor with a higher capacity
It’s essential to perform routine maintenance, including visual inspections, to catch and address these problems early. Additionally, consulting with a qualified technician or the pump manufacturer’s support team for more complex issues is advisable to ensure proper diagnosis and resolution.
Comparing Magnetic Drive Pumps & Industrial Centrifugal Pumps
In our CTM Magnetic Drive Pump, there’s no direct connection between the motor shaft and the impeller assembly, ensuring leak-free operation. In contrast, our CTI Industrial Centrifugal Pump uses a mechanical seal to protect the motor from fluid ingress.

The main difference lies in how power is transmitted to the impeller. The CTM utilises a magnetic coupling to rotate the impeller, driven by magnets with opposing polarities. Both pumps are Close-Coupled Centrifugal Pumps with options for different impellers, but the CTI can handle solids up to 6mm.
Both pumps excel in mechanical and corrosion resistance, with the CTM in Glass fibre reinforced Polypropylene or PVDF and the CTI in Glass blasted Stainless Steel AISI 316L. The CTM’s wetted components are non-metallic injection-moulded thermoplastics, enhancing corrosion resistance and reducing downtime.
Moreover, the CTM is a sealless pump, making it suitable for industries like Nuclear and Chemicals, where fluid leaks are a concern. This design eliminates the need for resins or glues, enhancing performance and safety at high temperatures.
The CTI is suitable for mild chemicals, oils, lubricants, coolants, detergents, partially solid-laden fluids and water transfer. It can also be ATEX-rated for pumping diesel, petrol and kerosene.
When choosing between these pumps, consider your specific application needs, fluid characteristics and industry requirements for optimal performance.
Range of Magnetic Drive Pumps
CTM Mag Drive Pump (Tapflo) Benefits:
- Ideal for low and normal viscosities
- No leakage due to the sealless design
- Efficient operation
- Reliable and compact design manufactured with fewer parts
- Manufactured from non-metallic injection-moulded thermoplastic
- Ideal for OEM applications
- Available as a portable unit that is safe for chemical transfer – find out more by visiting our CTM-IBC
- Highly customisable with many different executions available
Mag Drive Centrifugal Pump (Gemme Cotti) Benefits:
- Ideal for medium to heavy-duty applications
- High flow rate capacity
- Simplistic Centrifugal design that is greatly enhanced by the simplistic Mag Drive design
- Wide range of materials available
- Competitive pricing
- Compact and lightweight
- Features all the benefits of a Magnetically Driven Pump including sealless design
Mag Drive Regenerative Turbine Pump (Gemme Cotti) Benefits:
- Ideal for medium to heavy-duty applications
- Low/medium flow rate to medium/high head capacity
- Wide range of materials available
- Competitive pricing
- Features all the additional benefits of a Mag Drive Pump
- Used in various applications such as transfer or recirculation through heat exchangers, control valves, etc.
Mag Drive Rotary Vane Pump (Gemme Cotti) Benefits:
- Ideal for medium to heavy-duty applications
- Low flow rate to high head capacity
- Wide range of materials available
- Competitive pricing
- Features all the benefits of a Magnetically Driven Pump
- This type of Mag Drive Pump delivers a more forgiving pump technology and is typically used in high-pressure applications in industries such as the Automotive, Air Conditioning and Chemical industries to name a few
In closing, Magnetic Drive Pumps offer a reliable, sealless solution for various industries, ensuring the safe and efficient handling of fluids. Their innovative design, leak-free operation and versatile applications ensure that both process safety and productivity are enhanced.